What Is WORKDAY.INTL Excel Function?
The WORKDAY.INTL function in Excel is a powerful tool that allows professionals to calculate future or past dates excluding specified holidays and weekends, unlike the regular WORKDAY function, which considers only weekends (Saturday and Sunday) as non-working days, WORKDAY.INTL enables users to define their own set of non-working days using a custom string of their choice.
This flexibility makes it ideal for international businesses operating in different regions and jurisdictions with diverse public holidays and weekend arrangements. With this function, professionals can accurately project project milestones, delivery dates, or timelines by factoring in relevant holidays and weekends specific to each location.
The following example highlights the powerful functionality of the WORKDAY.INTL Excel function

Now, it’s time to enter the formula. The complete formula in cell C2 is:
=WORKDAY.INTL(A2, B2).
The resulting value will be promptly displayed in cell C2, as beautifully depicted in the accompanying image.

Table of contents
Key Takeaways
- The WORKDAY.INTL function in Excel is an advanced version of the WORKDAY function that allows customization of weekend parameters.
- It helps us determine a future or past date based on a specific number of working days and also considers weekends.
- Additionally, we can use this function to add or subtract days from a given date.
- Microsoft Excel stores dates as sequential serial numbers, enabling their utilization in calculations.
- By default, the serial number 1 corresponds to January 1, 1900, while January 1, 2018, is represented by the serial number 43,101. This is because it is precisely 43,101 days after January 1, 1900.
Syntax

start_date: This is the required argument. This field requires a valid date in the Excel format to be entered.
days: This is the required argument. This parameter indicates the number of working days that should be counted before or after the start date.
weekend: This is the optional argument. By utilizing this option, you can define which days of the week should be considered as weekends.
holidays: This is the optional argument. This field allows you to exclude certain dates or a range of dates from the working calendar.
How To Use WORKDAY.INTL Function In Excel? (With Steps)
To effectively utilize the WORKDAY.INTL function in Excel, follow these steps.
#1 – Access From The Excel Ribbon
Step 1: Choose the empty cell which will contain the result. Go to the Formulas tab and click it.
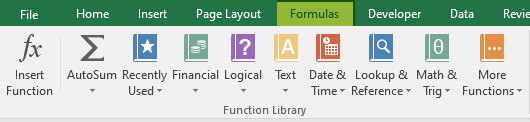
Step 2: Select the Date & Time option from the list.

Step 3: Select the WORKDAY.INTL from the drop-down menu.
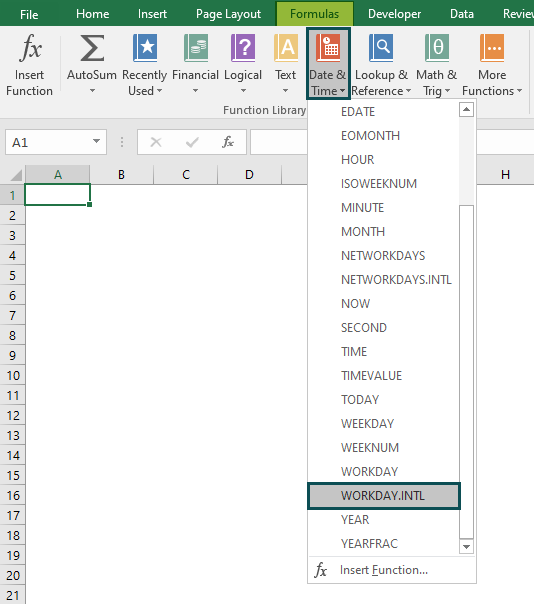
Step 4: A window called Function Arguments appears. As the number of arguments, enter the value in the start date, days, weekend, and holidays.
Select OK.
#2 – Enter The Worksheet Manually
Step 1: Select an empty cell for the output. Type =WORKDAY.INTL() in the selected cell. Alternatively, type =W and double-click the WORKDAY.INTL function from the list of suggestions shown by Excel.

Step 2: Press the Enter key to get the result.

Examples
Example #1 – Calculate The Workday With Custom Weekends And Exclude Holidays
In the following example, we will explore and apply the concept of the WORKDAY.INTL Excel function. Let’s calculate the workday with custom weekends and exclude holidays in the following scenario:
The data is:
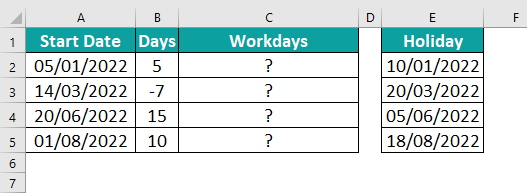
To calculate the desired output in cell C2, please follow these steps:
Step 1: Begin by selecting the cell where you wish to enter the formula and calculate the result. For this demonstration, let’s choose cell C2. Enter the formula as follows:
=WORKDAT.INTL(A2,B2,3,$E$2:$E$5).

Step 2: Once you have entered each value in the previous step, press the Enter key. The resulting value can be seen in cells C2 to C5.

By following these steps, we have calculated the workday with custom weekends and excluded holidays using the WORKDAY.INTL Excel function and obtain the desired outcome.
Example #2 – Generate A List Of Upcoming Workdays
In this example, we’re going to explore and apply the concept of the WORKDAY.INTL Excel function. Firstly, calculate today’s date as shown in cell B1, then let’s Generate a List of Upcoming Workdays using today’s date in the following scenario:
The data is:

To calculate the desired output in cell B2, follow these steps:
Step 1: Start by selecting the cell where you want to enter the formula and calculate the result. Let’s choose cell B2. Enter the formula as follows:
=WORKDAT.INTL($B$1,A4,1).

Step 2: After entering each value in the previous step, press the Enter key. The resulting value can be seen in cells B4 to B8.
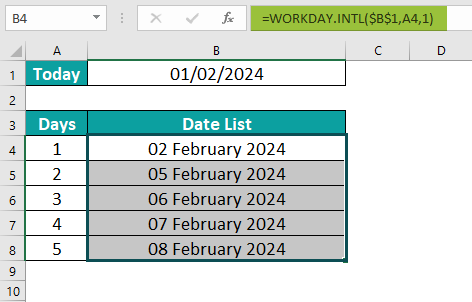
By following these steps, we have successfully Generated a List of Upcoming Workdays using the WORKDAY.INTL Excel function to obtain the desired outcome.
Example #3 – Project Task Dates With WORKDAY
In this example, we will delve into and apply the concept of the WORKDAY.INTL Excel function. Let’s calculate the Project Task Dates with WORKDAY in the following scenario:
The data is:

To calculate the desired output in cell D5, follow these steps:
Step 1: Begin by selecting the cell where you wish to enter the formula and calculate the result. For this demonstration, let’s choose cell D5. Enter the formula as follows:
=WORKDAY.INTL(MAX(B4,$B$2),SUM(C4)1).
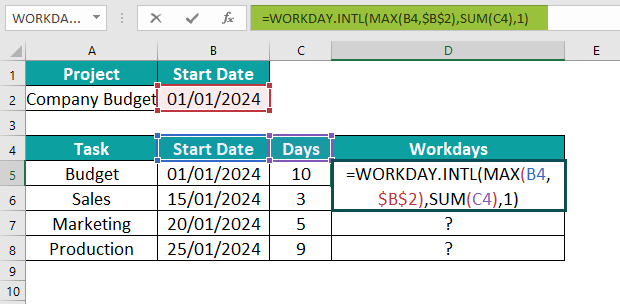
Note: The purpose of using the MAX and SUM functions with the WORKDAY.INTL function in Excel is to effectively calculate and manage workdays within a specific interval while considering custom weekends and holidays. The MAX excel function when combined with the WORKDAY.INTL function allows users to determine the latest date within a range, ensuring accurate scheduling. This is particularly useful when dealing with project deadlines or delivery dates. On the other hand, the SUM function can be employed to add multiple instances of workdays together, providing an aggregated count of total working days within a given time frame.
Step 2: Once you have entered each value in the previous step, press the Enter key. The resulting value can be seen in cells D5 to D8.

By following these steps, we have successfully calculated the Project Task Dates with WORKDAY, using the WORKDAY.INTL Excel function to achieve the desired outcome.
WORKDAY.INTL Excel Function Vs WORKDAY Excel Function
The WORKDAY.INTL and WORKDAY functions in Excel are valuable tools for managing and calculating workdays. However, there are key differences between the two that users must be aware of in order to make informed decisions about which function to utilize.
- The primary discrepancy lies in their ability to handle weekends and nonstandard workdays.
- While the WORKDAY excel function only considers Saturday and Sunday as weekends, the WORKDAY.INTL function allows users to customize which days of the week should be considered weekends or non-working days. This means that with WORKDAY.INTL, one can accurately calculate workdays based on varying weekend configurations across different countries or organizations.
- Additionally, the WORKDAY.INTL function also enables users to exclude specific holidays from calculations by providing a list of holiday dates. Conversely, the WORKDAY function does not possess this functionality and is, therefore, more limited in its application when dealing with diverse work schedules or holidays outside of standard weekends.
Important Things To Note
- When the start_date exceeds the allowable range based on the current date, the WORKDAY.INTL function will generate the error value #NUM!.
- Similarly, if any date within the holidays parameter falls outside the acceptable range based on the current date, the WORKDAY.INTL function will also produce the error value #NUM!.
- In the event that the addition of the day-offset to the start_date results in an invalid date, the WORKDAY.INTL function will once again return the error value #NUM!.
- Should the weekend string provided be of an incorrect length or contain invalid characters, the WORKDAY.INTL function will yield the error value #VALUE!.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The purpose of using the WORKDAY.INTL function in Excel is to calculate the date that falls a specified number of workdays before or after a given date, considering non-standard weekends and holidays.
The following example showcases the WORKDAY.INTL Excel function. Let’s delve into the details. In the provided table, the data is organized as follows:

To calculate the desired output in cell C2, follow these steps:
Step 1: Select cell C2 and enter the formula,
=WORKDAY.INTL(A2,B2).
Step 2: Press the Enter key. The resulting value will be displayed in cells C2 to C5, as depicted in the accompanying image.

• Firstly, it requires the use of a date format recognized by Excel, so if the date input is not formatted correctly, the function will return an error.
Additionally, the function can only calculate workdays within a range of 1st January 1900 to 31st December 9999. Therefore, any dates outside this range will not produce accurate results.
• Another limitation is that it cannot handle non-standard workweeks or holidays that vary from year to year. This means that if there are irregular working days or public holidays that change annually, the function may not provide the desired outcome accurately.
One can activate the WORKDAY.INTL function in Excel using the following steps:
• Choose the empty cell which will contain the result.
• Go to the “Formulas” tab and click it.
• Select the “Date & Time” group.
• A window called “Function Arguments” appears.
• As the number of arguments, enter the value in the “start date,” “days,” “weekend,” and “holidays.”
• Select OK.
Download Template
This article must help us understand the WORKDAY.INTL Excel Function’s formula and examples. You can download the template here to use it instantly.
Recommended Articles
Guide to WORKDAY.INTL function in Excel. Here we learn how to use WORKDAY.INTL Function in excel with step by step examples and a downloadable template. You can learn more from the following articles –

Leave a Reply