What is VBA RoundDown Function in Excel?
The VBA RoundDown function in excel is used to round a number down to a specified number of digits. It is similar to the Round function, but instead of rounding to the nearest value, it always rounds down.
See the example below on using the VBA RoundDown function.:

In this subroutine, the RoundDown function is used to round the given number down to 2 decimals. These values are then printed in the Message Box to show to the user.

Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- The RoundDown function is used to round a number down to a specified number of digits.
- Unlike the Round function, which rounds to the nearest value, RoundDown always rounds down to the nearest value.The RoundDown function returns a numeric value.
- RoundDown can be useful when you need to truncate decimal places while ensuring that the number is always rounded down.
- Be careful with negative numbers. RoundDown still rounds down, but the result might not be what you expect for negative numbers. Always test with your specific use case.
Excel VBA 5-in-1 Course Bundle – (30+ Hours of Expert-Led Training)
If you want to learn Excel and VBA professionally, then the Excel VBA 5-in-1 Course Bundle (30+ hours) is the perfect solution. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, this bundle covers it all – from Basic Excel VBA to Event Automation, Error Handling, Email Automation, and real-world applications with downloadable templates.
Syntax
The Syntax of the RoundDown function is:
WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(number, num_digits)
Or
Application.WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(number, num_digits)
Where,
- number is the number you want to round down.
- num_digits is the number of digits to which you want to round down.
How to use VBA RoundDown Function?
Learn how to use the VBA RoundDown function by following the steps below.
Step 1: Select the “Developer” option on the Excel toolbar. If it’s not there, go to “File”> ”Options”> ”Customize Ribbons” and enable “Developer.”

Under “Developer,” select “Visual Basic” to open the VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) editor.

Here, select “Insert” on the toolbar, and then select “Module” to create a new module where you can code the different examples of the RoundDown function.

Step 2: Define a subprocedure to remove the decimal values from the PI value.

Step 3: Define the PI value using the PI function available in the WorksheetFunction module.

Step 4: Round the value of PI to the last four decimal points by calling the VBA RoundDown function.

Step 5: Print the rounded value and the original value to show the difference.
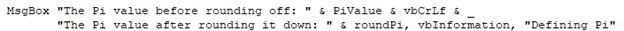
In VBA, vbCrLf is a constant representing a newline character sequence. It’s employed to incorporate line breaks or carriage returns within strings, facilitating the creation of multiline text or formatting output to include line breaks in excel.
The “vbInformation” is a keyword used in Excel VBA to add an “information” icon while printing the Message Box.
Code:
Sub DecreaseDecimalDigits()
Dim PiValue As Double
PiValue = WorksheetFunction.Pi
Dim roundPi As Double
roundPi = WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(PiValue, 4)
MsgBox “The Pi value before rounding off: ” & PiValue & vbCrLf & _
“The Pi value after rounding it down: ” & roundPi, vbInformation, “Defining Pi”
End Sub
Step 5: Click “F5” or the “Run” icon on the activity bar in the VBA Editor.

Now you know the basics of using the function VBA RoundDown.
Examples
Let us look at some interesting examples of what you can do using the VBA RoundDown function.
Example #1
Suppose you have a number in your worksheet. You want to convert that number to a whole number. To do that, you can use the VBA RoundDown function and print it in the adjacent cell.

Step 1: Define a subroutine to convert a given number with decimals to a whole number.

Step 2: Take the value from the cell and store it in a Double variable.

Step 3: Calculate the Rounded value. If you want no decimals, set the “num_digits” parameter as 0.

Step 4: Set the adjacent cell value as the number that has been rounded. The adjacent cell is cell “C3”.

Step 5: Define a Message Box function to print the confirmation of rounding off to a whole number.

The “vbInformation” icon is used to print an ‘i’ icon on the left-hand side of the Message Box.
Code:
Sub ConvertToWholeNumber()
Dim original As Double
original = Range(“B3”).Value
Dim round As Double
round = WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(original, 0)
Range(“C3”).Value = round
MsgBox “Successfully converted to a whole number!”, vbInformation
End Sub
Step 7: Run the above subroutine. Then, go back to the worksheet to see the changes.


Example #2
You are given a number in the worksheet and told to round it off to the nearest 100. There are a multitude of ways you can do this, but the easiest way to do so is to call the VBA RoundDown function to do the same.

Step 1: Name the subroutine to round off the number to the nearest hundreds value.

Step 2: Initialize a double variable and assign it the value from cell “B7”.

Step 3: Initialize another double variable. Set the number rounded off to the nearest hundred by setting the “num_digits” parameter as ‘-2’.

Step 4: Print the rounded value adjacent to the original value. In this case, it is printed in cell “C7”.

Step 5: Print the confirmation message using a Message Box function.

To make the Message Box more visually appealing, you can add an icon to it using the predefined keywords. In this case, the keyword “vbInformation” is used.
Code:
Sub ConvertToNearestHundred()
Dim ori As Double
ori = Range(“B7”).Value
Dim round As Double
round = WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(ori, -2)
Range(“C7”).Value = round
MsgBox “Successfully rounded ” & ori & ” to the nearest hundreds value!”, vbInformation
End Sub
Step 6: Run the above subroutine. Then go back to the worksheet to see the changes.


Example #3
Consider that you have a number with a lot of decimal values. For your calculations, you decide it is easier to round off to the nearest tenth decimal since accuracy doesn’t matter in what you’re doing. The value can be rounded off using the VBA RoundDown function.

Step 1: Start by naming the sub-procedure to round off the given value to the nearest tenth decimal.

Step 2: Assign a double value to store the given value. A double datatype can hold in more decimals compared to other data types.

Step 3: Define the rounded value with its “num_digits” feature set to 1 for only one decimal digit. This value is then stored in a double datatype variable.

Step 4: Store this decimal number in one of the worksheet cells. In this example, the cell “C11” is being used.

Step 5: Declare a message box printing the original value to compare to the changes caused by the VBA RoundDown function.

Code:
Sub ConvertToNearestTenth()
Dim org As Double
org = Range(“B11”).Value
Dim round As Double
round = WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(org, 1)
Range(“C11”).Value = round
MsgBox “Successfully rounded ” & org & ” off to 1 decimal value!!”, vbInformation
End Sub
Step 6: Run the subroutine to reduce the number of decimals to only one decimal number.


Example #4
For example, you use the RAND() function in Excel and generate a random number between 0 and 1. You want to use this for calculations, but you want to reduce the number of decimals for lower precision and to make the calculations easier.

You can use the VBA RoundDown function to perform this functionality.
Step 1: Begin the process by naming the subroutine to perform the functionality to reduce the given value to 2 decimals.

Step 2: Take the cell with the random value and store it in a double variable.

Step 3: To round the number to the first two decimal places, you need to set the “num_digits” parameter as ‘2’.

Store the resulting rounded variable in a new double variable explicitly defined for this.
Step 4: Paste the value in the double variable in the worksheet. Here, it is pasted in cell “C15”.

Step 5: Create a message box to print the values before and after rounding it.

Code:
Sub ConvertToOnlyTwoDecimalPlaces()
Dim orig As Double
orig = Range(“B15”).Value
Dim round As Double
round = WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(orig, 2)
Range(“C15”).Value = round
MsgBox “Successfully rounded ” & orig & ” off to 2 decimal values as ” & round, vbInformation
End Sub
Step 6: Go to the Worksheet and select “Macros” under the “Developer” tab.

Select the macro you want to run in the options.

After running the macro, the output can be seen in the Worksheet.


Important Things To Note
- Always specify the number of digits to which you want to round down when using the VBA Rounddown function. This ensures clarity and precision in your calculations.
- Ensure that the VBA data type of the input number is appropriate for your use case. RoundDown typically works with numeric data types such as Double or Integer.
- Avoid confusing the RoundDown function with other rounding functions like Round, RoundUp, or Int. Also, avoid using RoundDown for currency handling or financial calculations where precision is crucial.
- Validate the input values before using the VBA RoundDown function to ensure they are within the acceptable range and type for your calculations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
RoundDown always rounds down to the nearest value.
The Round function rounds to the nearest value, with halves rounded away from zero. For example, look at the number below.
originalNumber = 2134.5778
roundedNumber = WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(originalNumber, 2) Debug.Print “Rounded down result: ” & roundedNumber
roundedNumber = WorksheetFunction.round(originalNumber, 2) Debug.Print “Rounded down result: ” & roundedNumber
Yes, the VBA RoundDown function can be used with negative numbers in VBA, but it always rounds down, regardless of the sign of the number.
If you use negative values for the ‘num_digits’ argument, it will round down the numbers on the left-hand side of the decimals, that is the whole number part. For example, to round a number to the nearest hundreds value, you define the num_digits argument as ‘-2’.
originalNumber = 2134.5778
roundedNumber = WorksheetFunction.RoundDown(originalNumber, -2) MsgBox “Rounded down result: ” & roundedNumber
Yes, the RoundDown function can be nested within other functions in VBA. You can perform multiple calculations in VBA using the RoundDown function.
originalNumber = 12.345
roundedNumber = RoundDown(Sqr(originalNumber), 2)
Here, the VBA Sqr() function is used to find the Square Root of the number and the value is rounded down to 2 decimal points.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VBA ROUNDDOWN. Here we learn how to use VBA RoundDown function using syntax with step by step examples. You can learn more from the following articles –

Leave a Reply